Effect of permafrost properties on gas hydrate petroleum system in the Qilian Mountains, Qinghai, Northwest China
文献类型:期刊论文
| 作者 | Wang PK; Zhang XH(张旭辉) ; Zhu YH ; Zhu YH ; Li B; Huang X ; Li B; Huang X ; Pang SJ; ZhangS; Lua C; Xiao R ; Pang SJ; ZhangS; Lua C; Xiao R
|
| 刊名 | Environmental Science Processes & Impacts
 |
| 出版日期 | 2014-12 |
| 卷号 | 16期号:12页码:2711-2720 |
| 通讯作者邮箱 | wangpk@cags.ac.cn |
| ISSN号 | 2050-7887 |
| 产权排序 | [Wang, Pingkang; Zhu, Youhai; Huang, Xia; Pang, Shouji; Zhang, Shuai; Lu, Cheng] China Geol Survey, Oil & Gas Survey, Beijing 100029, Peoples R China; [Zhang, Xuhui] Chinese Acad Sci, Inst Mech, Beijing 100190, Peoples R China; [Li, Bing] Jilin Univ, Coll Construct & Engn, Changchun 130021, Peoples R China; [Xiao, Rui] Chinese Acad Geol Sci, Inst Mineral Resources, Beijing 100037, Peoples R China |
| 通讯作者 | Wang, PK (reprint author), China Geol Survey, Oil & Gas Survey, Beijing 100029, Peoples R China. |
| 合作状况 | 国内 |
| 中文摘要 | The gas hydrate petroleum system in the permafrost of the Qilian Mountains, which exists as an epigenetic hydrocarbon reservoir above a deep-seated hydrocarbon reservoir, has been dynamic since the end of the Late Pleistocene because of climate change. The permafrost limits the occurrence of gas hydrate reservoirs by changing the pressure–temperature (P–T) conditions, and it affects the migration of the underlying hydrocarbon gas because of its strong sealing ability. In this study, we reconstructed the permafrost structure of the Qilian Mountains using a combination of methods and measured methane permeability in ice-bearing sediment permafrost. A relationship between the ice saturation of permafrost and methane permeability was established, which permitted the quantitative evaluation of the sealing ability of permafrost with regard to methane migration. The test results showed that when ice saturation is >80%, methane gas can be completely sealed within the permafrost. Based on the permafrost properties and genesis of shallow gas, we suggest that a shallow “gas pool” occurred in the gas hydrate petroleum system in the Qilian Mountains. Its formation was related to a metastable gas hydrate reservoir controlled by the P–T conditions, sealing ability of the permafrost, fault system, and climatic warming. From an energy perspective, the increasing volume of the gas pool means that it will likely become a shallow gas resource available for exploitation; however, for the environment, the gas pool is an underground “time bomb” that is a potential source of greenhouse gas. 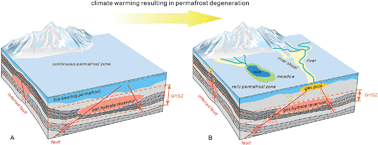 |
| 学科主题 | 渗流 |
| 分类号 | 二类/Q2 |
| 收录类别 | SCI |
| 资助信息 | We thank the anonymous reviewers and publishing editor (Dr Jack Busby from Royal Society of Chemistry) for their many useful comments and suggestions, which helped improve the paper. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no.: 41102021, 41202099), National Special Research Fund (Gas Hydrate Resource Exploration and Production Testing Project) (Grant no.: GZHL20110308, GZH201400301), and Chinese Polar Environment Comprehensive Investigation & Assessment Programmes (Grant no.: CHI-NARE2014-04-05). |
| 原文出处 | http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlepdf/2014/em/c4em00482e |
| 语种 | 英语 |
| WOS记录号 | WOS:000345454100005 |
| 公开日期 | 2014-12-02 |
| 源URL | [http://dspace.imech.ac.cn/handle/311007/49357]  |
| 专题 | 力学研究所_流固耦合系统力学重点实验室(2012-) |
| 推荐引用方式 GB/T 7714 | Wang PK,Zhang XH,Zhu YH,et al. Effect of permafrost properties on gas hydrate petroleum system in the Qilian Mountains, Qinghai, Northwest China[J]. Environmental Science Processes & Impacts,2014,16(12):2711-2720. |
| APA | Wang PK.,Zhang XH.,Zhu YH.,Li B.,Huang X.,...&Xiao R.(2014).Effect of permafrost properties on gas hydrate petroleum system in the Qilian Mountains, Qinghai, Northwest China.Environmental Science Processes & Impacts,16(12),2711-2720. |
| MLA | Wang PK,et al."Effect of permafrost properties on gas hydrate petroleum system in the Qilian Mountains, Qinghai, Northwest China".Environmental Science Processes & Impacts 16.12(2014):2711-2720. |
入库方式: OAI收割
来源:力学研究所
其他版本
除非特别说明,本系统中所有内容都受版权保护,并保留所有权利。

